Paramedics are the front line of emergency medical care. Whether responding to car accidents, heart attacks, or natural disasters, these professionals are trained to make life-saving decisions under pressure. If you’re interested in a rewarding career where you can make a real difference, becoming a paramedic might be for you.
Here’s a breakdown of what it takes to become a paramedic, including training, licensing, job opportunities, and salary expectations.
What is a paramedic?
A paramedic is a highly trained healthcare professional who provides advanced pre-hospital medical care in emergencies. Paramedics are typically part of emergency medical services (EMS) teams and respond to 911 calls involving serious injury or illness.
Unlike emergency medical technicians (EMTs) who are only trained to provide basic life support, paramedics can administer medications, start IV lines, interpret EKGs and perform advanced airway management. They work alongside firefighters, police officers and hospital staff to stabilize and transport patients.
How do I train to become a paramedic?
The first step in becoming a paramedic is to earn your EMT license, which requires 120-200 training hours on average. EMTs may still respond to 911 calls in an ambulance, but are trained to assist paramedics with advanced life-saving techniques rather than perform them on their own. Depending on what course you enroll in, it can take anywhere from a few weeks to about six months to complete.
Once you receive your EMT certification, you then have the option of enrolling in paramedic school. Paramedic training will take anywhere from six months to about two years to complete, but many students continue to work as an EMT while finishing their classes. Paramedic certification programs are offered at community colleges, technical schools and some universities. The training includes both classroom instruction and hands-on clinical practice.
Typical paramedic coursework includes:
- Anatomy and physiology
- Advanced life support techniques
- Trauma management
- Pharmacology
- Cardiology
- Emergency childbirth
- Patient assessment
- Clinical and field internships
How long does it take to become a paramedic?
If you are starting your paramedic career journey without any medical training, it can take 2-3 years to earn your paramedic license, alotting for six months to earn your EMT certification and then an additional two years, give or take, to complete paramedic training:
- Step 1 — EMT certification: ~6 months
- Step 2 — Paramedic training program: 12–18 months
- Step 3 — Licensing and exams: 1–3 months
How long is paramedic school?
Depending on the program, paramedic school can take up to two years to complete. Some accelerated programs may allow you to finish more quickly, while part-time programs may take longer.
Where can I look for a paramedic job?
Paramedics are in high demand across the U.S., especially in rural and underserved areas. You can find paramedic jobs with:
- Ambulance services
- Private EMS agencies
- Fire departments
- Hospitals and trauma centers
- Air medical transport services
- Private event and industrial safety teams
- State and local government agencies
Look for listings on job boards on industry-specific sites like EMS1, as well as traditional sites, like Indeed or Glassdoor.
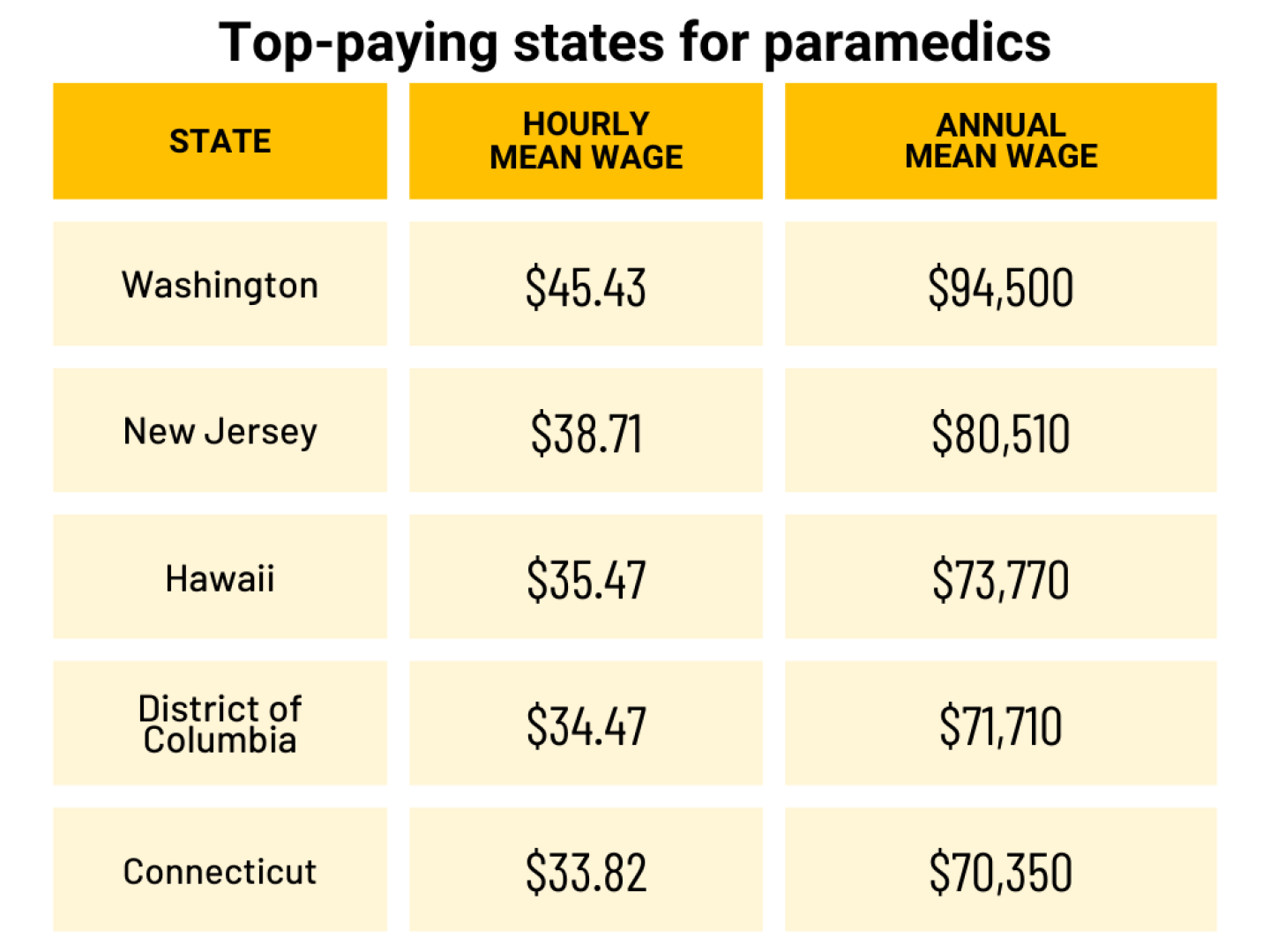
What is a paramedic’s salary?
Paramedics, due to their higher level of training and responsibility, typically earn a higher salary compared to EMTs. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor and Statistics, the annual median wage for a paramedic is $53,180 as of May 2023, with the lowest 10% earning less than $38,520 and the highest 10 % earning more than $79,430.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the fives states with the highest-paid EMT salary are Hawaii, Alaska, the Distric of Columbia, California and Illinois.
What is a paramedic license?
A paramedic license is the legal authorization issued by a state’s EMS regulatory body that allows an individual to practice as a paramedic. After passing the NREMT exam, you must apply for licensure in the state where you plan to work.
Each state has its own licensing process, but most require:
- Proof of paramedic education
- Current CPR certification
- NREMT exam results
- Background check
- Continuing education for license renewal
What is the difference between a paramedic license and a paramedic certification?
Understanding the difference between paramedic certification and paramedic licensure is key:
- Paramedic certification: This refers to passing the National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT) exam. It validates your knowledge and skills at a national level.
- Paramedic license: This is granted by an individual state and gives you the legal right to work as a paramedic in that state.
Think of it this way: Certification proves your competence, while licensure grants you permission to practice.
While the requirements to be a paramedic are arduous, the work itself can be extremely rewarding. Being a paramedic requires a dedication to the job that makes it more of an avocation than a vocation. It definitely isn’t the right choice for everybody, but for many, it’s the job of a lifetime.
This article, originally published in September 2016, has been updated.